What You’ll Learn
This article explains why the old “throw it over the wall” model stalls releases, how Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) turn slow hand-offs into fast, reliable pipelines, and why devops for cloud management has become the backbone of modern cloud delivery. You will discover proven ways to cut deployment errors, see which metrics truly matter to CTOs and product leaders, and explore short real-world stories that bring cloud DevOps from theory into everyday practice.
The Wall of Confusion: Where Great Code Goes to Die
Developers want to merge features quickly, while operations teams focus on uptime and security. When code is “tossed” from dev to ops without context, three predictable problems surface:
-
Defects linger because QA receives code too late
-
Releases bunch up, increasing blast radius if something fails
-
Blame cycles erode trust between teams
Together, these issues form the notorious Wall of Confusion. Tearing it down is the first step toward reliable cloud delivery.
Teams that replace siloed workflows with shared pipelines report dramatic gains. One organization that moved its monolith to Azure Platform as a Service saw a 228 % return on investment in three years and reached payback in just 15 months.
Collaboration must be baked into both culture and tooling before any speed advantage materializes. For a practical look at breaking down these barriers and streamlining cloud pipelines, see Tech-Driven DevOps: How Automation is Changing Deployment.
Real-World Example
A European fintech replaced weekly change-approval meetings with a shared Slack channel tied to its CI server. Developers saw deployment logs in real time, while operations posted infrastructure metrics alongside. Within two sprints, incident post-mortems shifted from “who broke it?” to “how do we automate the fix?”
Continuous Integration: Small Batches, Fast Feedback
Continuous Integration means every commit is merged to the main branch only after an automated test suite passes. Merging many small changes instead of one giant release offers clear benefits:
-
Fewer merge conflicts because branches live for hours, not weeks
-
Rapid feedback on defects while the context is fresh
-
A single source of truth that everyone trusts
Automated builds should cover unit, integration, and security scans. Popular DevOPS tools management stacks include GitLab CI, GitHub Actions, CircleCI, and Jenkins with shared libraries.
When engineers see red builds quickly, they avoid the expensive rework that haunts late-stage QA. The 2024 DORA report showed that code review speed rises 3.1% when teams embrace AI assistance, yet 39 % still distrust automated suggestions. Visibility and repeatable pipelines help bridge that trust gap.
To maximize the benefits of CI, it's worth exploring workflow optimizations discussed in The Managed DevOps Cheat Sheet: how to cut App Development Time and Costs by 80% about devops technology.
Ending this stage, remember that CI is pointless without the next step: delivering the approved build to customers.
Continuous Deployment: Shipping Confidently, Shipping Often
Continuous Deployment extends CI by pushing every green build into production (or at least into a staging environment) through automated steps:
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scripts create or patch cloud resources
-
Canary or blue-green strategies route a small user slice first
-
Rollbacks are instant, using previous container images or configurations
For leadership, CD directly translates to reduced time-to-market. A metro-retail chain that migrated to Azure PaaS reported a 50% increase in development speed after switching to automated deployments, while trimming 40 % of infrastructure costs.
CD works only if the underlying cloud environment is reproducible on demand, which is why understanding best practices around IaC and Integrated Security is key. For more, explore Cloud Support: How Managed DevOps Keeps Your Business Online 24/7.
Real-World Example
A U.S. media platform used AWS CodePipeline plus CloudFormation. Each merge to main deployed to a staging account, ran synthetic user tests, and, on success, triggered a production push. Release frequency jumped from twice a month to 20 times per day without a single unplanned rollback in the first quarter.
Automation as the Backbone of Cloud Performance and Reliability
Cloud services change daily. Manual changes cannot keep up. DevOps infrastructure automation uses declarative files to describe servers, databases, networks, and permissions. Benefits include:
-
Consistency: the same script builds dev, staging, and prod
-
Speed: environment creation drops from hours to minutes
-
Auditability: every change is version-controlled
For a detailed breakdown of how automation, environment consistency, and cross-cloud management work in practice, see Cloud Services and DevOps.
VMware found that its Cloud Foundation customers experienced a 77 % average operational efficiency gain and a five-fold reduction in downtime after adopting automated network operations.
Transitioning onward, automation is only powerful when paired with clear techniques to prevent slip-ups during releases.
Field-Tested Techniques to Shrink Errors and Accelerate Release Cycles
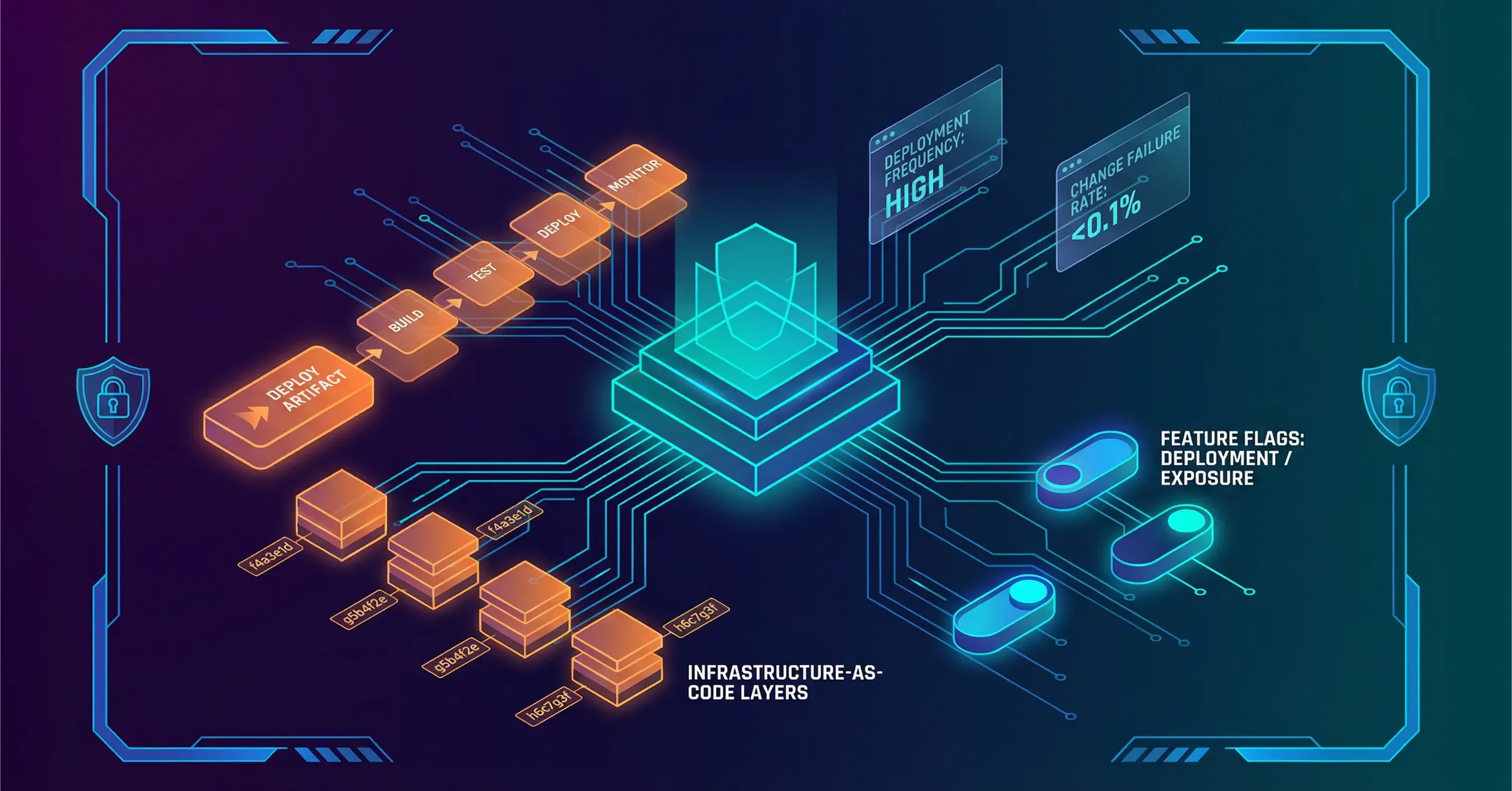
High-performing teams layer several executable policies on top of CI/CD and automation:
-
Maintain a single deployable artifact per commit to ensure parity across stages
-
Write idempotent IaC scripts so reruns never harm running workloads
-
Tag every infrastructure change with a commit hash for traceability
-
Use feature flags to decouple code deployment from feature exposure
-
Collect metrics such as deployment frequency and change failure rate, then publish them on an internal dashboard
The importance of robust observability and automation guardrails is further illustrated in Balancing Cloud Computing and Cloud Security: Best Practices.
Platform engineering is maturing quickly. In Puppet’s 2024 survey, 70% of respondents said their platform work began at least three years ago and the same share built security into the platform from day one. That long horizon highlights the value of foundational investments rather than last-minute fire drills.
Before wrapping up, remember that no toolset eliminates the need for healthy culture. Metrics should inform coaching, not punishment.
Cloud DevOps in One Paragraph
Cloud DevOps combines shared culture, Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, and infrastructure automation so that every code change is built, tested, and promoted through reproducible pipelines with minimal human intervention, cutting release latency from weeks to minutes while raising system reliability.
Conclusion
The journey from code to customer once trudged through hand-offs and late-night releases. DevOps for cloud management replaces that grind with collaborative pipelines, automated tests, and self-documenting infrastructure that scales with the business. Companies that embrace CI, CD, and infrastructure as code are already posting triple-digit ROI, multi-fold efficiency gains, and dramatic drops in downtime. For technology leaders, the message is clear: automate the path, nurture the culture, and let innovation flow without walls. For a step-by-step roadmap on how top-performing businesses are embracing these principles, see The Managed DevOps Cheat Sheet: how to cut App Development Time and Costs by 80% about devops technology.