What You Will Learn
In the next few minutes we will show how digital immunity differs from classic cybersecurity, why automated recovery, immutable backups, and blast-radius containment form its backbone, and how a mid-sized enterprise can fund the shift by reframing “security spend” as a business continuity investment. Real-world cases and 2025 market data ground every step.
From Cybersecurity to Digital Immunity
Cybersecurity tries to keep every threat out. Digital immunity starts with the assumption that something will get in and designs the environment so it survives the breach.
Digital immunity rests on three pillars:
-
Automated recovery that brings systems back online without human tickets
-
Immutable backups that cannot be altered, deleted, or encrypted by attackers
-
Blast-radius containment that isolates infected workloads before lateral movement begins
The idea mirrors the human body. You still wash your hands, but you know germs slip through, so you rely on an immune system that detects, isolates, and repairs damage in minutes.
Boards are listening. The worldwide IT services market reached nearly US$1.50 trillion in 2025, yet more money is flowing into resilience projects than into fresh firewalls. Eighty-four percent of firms already report rising network outages that erode trust. Immunity has become the new uptime metric.
The next sections show how to build each pillar, one decision at a time. For a deep dive on how a unified security posture supports these pillars across cloud and hybrid environments, see Cloud Managed Security: Unified Security Strategy for Cloud and Hybrid Enviroinments.
How Immutable Backups Saved a Hospital
A regional healthcare chain suffered a ransomware hit that encrypted 40 TB of patient images. Immutable snapshots on a disconnected storage tier let them restore radiology services in 14 minutes, fast enough that clinicians never lost access. Patient appointments stayed on schedule, and the breach never made local news. Protection failed, but immunity kept the business alive. The following section explores the automation that made that 14-minute recovery possible.
Automated Recovery: Healing at Machine Speed
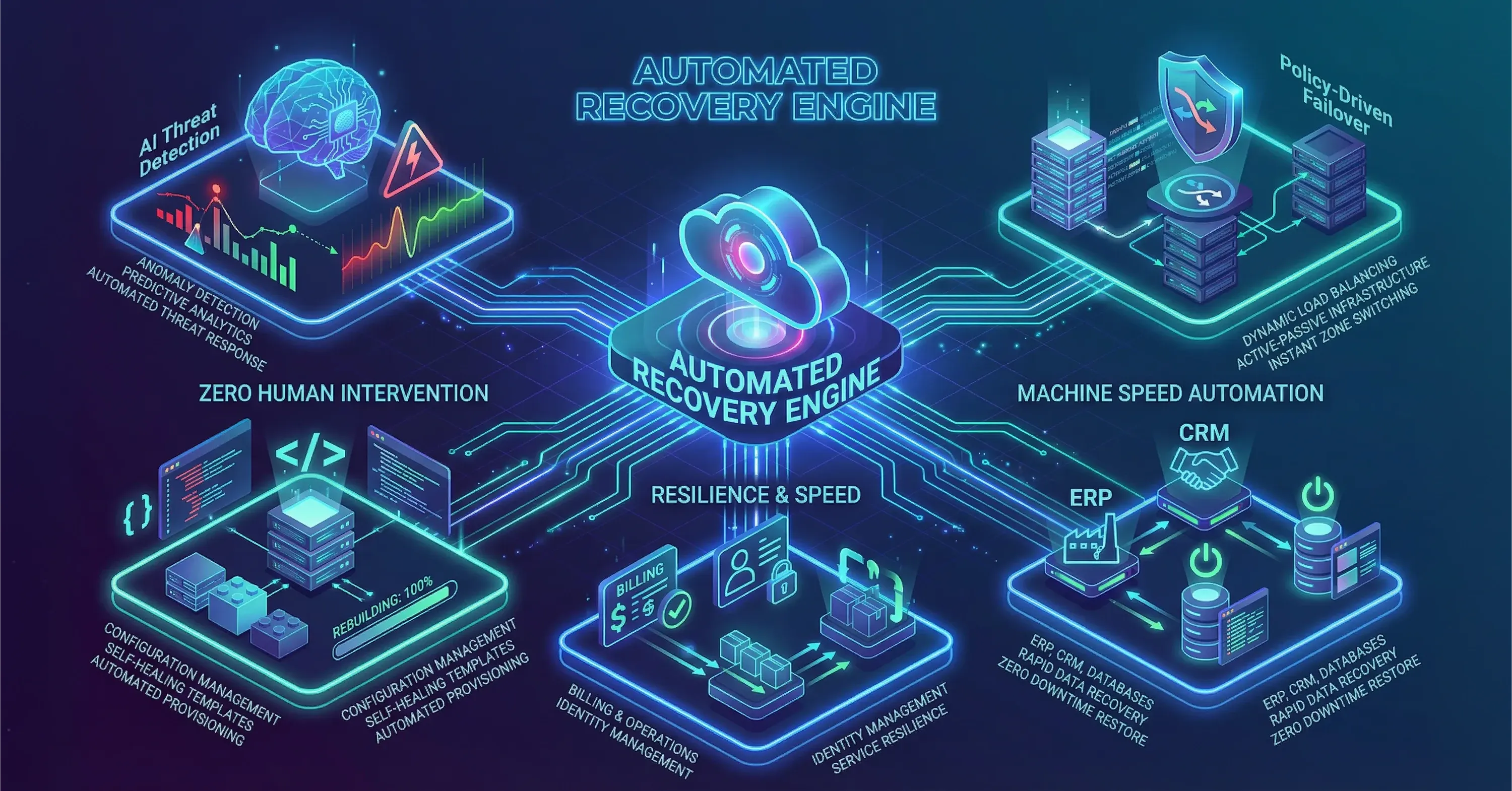
Humans do not type faster under stress. In 2026, adversaries script their attacks, so we script our defense.
Automated recovery combines:
-
Policy-driven failover that spins up clean virtual machines or containers in secondary zones
-
Infrastructure-as-Code templates stored in secure repositories, ready to redeploy a full stack on demand
-
AI detection models that trigger the workflow once abnormal behavior crosses a predefined threshold
Why the urgency? More than one-third of organizations lost US$1 million to US$5 million in outage-related revenue last year. Manual runbooks cannot preserve cash flow under that pressure.
For mid-sized enterprises, an attainable first step is to automate the restoration of core ERP or CRM systems, then extend the pattern across the portfolio.
Integration with IT and business services matters here. Recovery scripts must restore not only servers, but also service management queues, identity stores, and the billing platform that keeps invoices going out. Skipping those pieces means the lights are on yet revenue is still frozen.
A leading provider of managed IT services, offering comprehensive solutions for infrastructure management, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and business technology optimization, often bundles prebuilt recovery playbooks that clients can tailor, shrinking deployment time from months to weeks. For additional practical guidance on automating recovery, disaster restoration, and root cause analysis, read Cloud Support: How Managed DevOps Keeps Your Business Online 24/7.
Six-Minute Recovery Without Human Intervention
A logistics firm uses policy-driven snapshots for its warehouse management system. When an AI model flagged unusual database writes at 02:14 AM, the platform auto-switched traffic to a clean read replica, rebuilt the primary node from code, and resumed writes in under six minutes. Drivers never saw a delay in routing updates. Automation preserved the supply chain without waking an engineer. The next pillar ensures the data those scripts restore is untainted.
Immutable Backups and Blast-Radius Containment
If attackers can encrypt or delete your backups, recovery scripts have nothing to pull from. Immutable backups solve that by making every restore point read-only, versioned, and locked for a defined retention period.
Key design choices:
-
Write-once, read-many (WORM) storage or object-lock features in major clouds
-
Separate credentials so production admins cannot alter backups
-
Out-of-band replication to a secondary region or cloud account
Blast-radius containment complements immutability. The goal is to limit how far malware or a rogue script can travel.
Containment tactics:
-
Micro-segmentation that restricts east-west traffic inside the data center
-
Just-in-time access so privileged sessions expire automatically
-
Egress controls that block unexpected outbound connections
For a field-tested perspective on micro-segmentation, east-west containment, and the pitfalls of traditional defenses, explore Is Your Legacy Firewall Exposing Your Cloud? Cloud Security in Information Security.
Mid-sized companies often fear these tactics require hyperscale budgets, yet the market for outsourced expertise is exploding. The IT professional services sector is projected to grow by USD 657.9 billion between 2025 and 2029, which means competitive pricing and vertical-specific packages.
How Immutability Prevented Data Loss
A SaaS accounting vendor stores hourly database snapshots on object-lock buckets with a 45-day retention. When a disgruntled admin attempted to purge client ledgers, the system rejected the delete commands. Security then suspended the user account, and internal auditors confirmed no data loss. Customers never knew there was an incident. Immutability plus containment turned an insider threat into a non-event. Our final section explains how to position these investments as business continuity, aligning them with board priorities.
Turning Cost into Strategy: Business Continuity Metrics Boards Track
Boards approve budgets when they see an outcome tied to revenue. Cyber-resilience becomes a business continuity strategy when leaders express it in language a CFO trusts.
Translate technology into three metrics:
-
Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD): the longest a process can be offline before revenue impact turns critical
-
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): the targeted restoration window, measured in minutes or hours
-
Recovery Point Objective (RPO): the amount of data loss acceptable, often in seconds for financial systems
Framing resilience around MTD, RTO, and RPO connects IT alignment with corporate risk appetite. This echoes a TechRadar insight that CIOs are now “central influencers in digital transformation, responsible for aligning strategy, technology, and culture”.
Instead of endlessly adding point solutions, organizations are discovering the cost benefits of security delivered as a service. Why Security as a Service Is the Future of Cyber Defense unpacks the shift from tool sprawl to business outcome budgeting and predictable resilience investments.
Funding tips for mid-sized enterprises:
-
Reallocate part of the cyber-insurance premium toward automation tooling, lowering overall risk and future premiums
-
Consolidate overlapping security products, freeing operating budget for immutable storage
-
Use managed service contracts to convert capital expense into predictable monthly fees, leveraging the US$588.38 billion IT outsourcing segment recorded in 2025.
Done well, resilience planning supports not just security but broader business continuity, reducing the 3AM concerns that keep CEOs awake.
Turning RTO Into Revenue Protection
A regional retailer tied RTO improvements to projected weekend sales. Cutting the web-store RTO from four hours to 20 minutes protected an estimated $2.1 million in quarterly online revenue. That single metric unlocked board approval for immutable backup licensing and a managed recovery service.
What Is Digital Immunity? A Simple Definition for Business Leaders
Digital immunity is a cyber-resilience model that assumes breaches will occur and prioritizes three capabilities: automated recovery that restores systems without human intervention, immutable backups that attackers cannot alter or delete, and blast-radius containment that limits the spread of any compromise. The goal shifts from blocking every threat to ensuring business processes continue, which elevates cybersecurity from a cost center to a business continuity strategy.
Conclusion
Cyber-resilience is no longer about adding one more layer of protection. Boards in 2026 demand immunity: systems that heal, data that cannot be poisoned, and architectures that confine damage to a corner of the network. By combining automated recovery, immutable backups, and blast-radius containment - and by expressing their value in hard business continuity metrics - mid-sized enterprises can face AI-driven threats with confidence that the business will not stop, no matter what crosses the firewall.