Why ad-hoc controls crumble in hybrid and multi-cloud setups
Moving workloads to multiple public clouds, retaining on-prem systems, and embracing SaaS creates a maze of policies and consoles. Each platform ships its own firewall rules, IAM quirks, and logging formats. The result is uneven coverage and slower incident response.
- Conflicting policies: A port blocked in AWS might remain open in Azure, giving attackers an easy pivot.
- Visibility gaps: Native dashboards often show only their slice of the estate. Lateral movement across platforms goes unnoticed.
- Skill overload: Security teams must learn dozens of vendor-specific tools, increasing training cost and burnout.
- Audit headaches: Proving compliance to PCI DSS, HIPAA, or CMMC across mixed infrastructures becomes a spreadsheet nightmare.
According to a market report, the global cloud security market is projected at USD 19.71 billion in 2025 and will grow rapidly in the coming years. Spending is rising because organizations realise piecemeal defences no longer work.
Proper managed cloud security aggregates these controls into one strategy, slashing complexity and sealing cracks before attackers find them.
The pillars of a unified managed cloud security posture
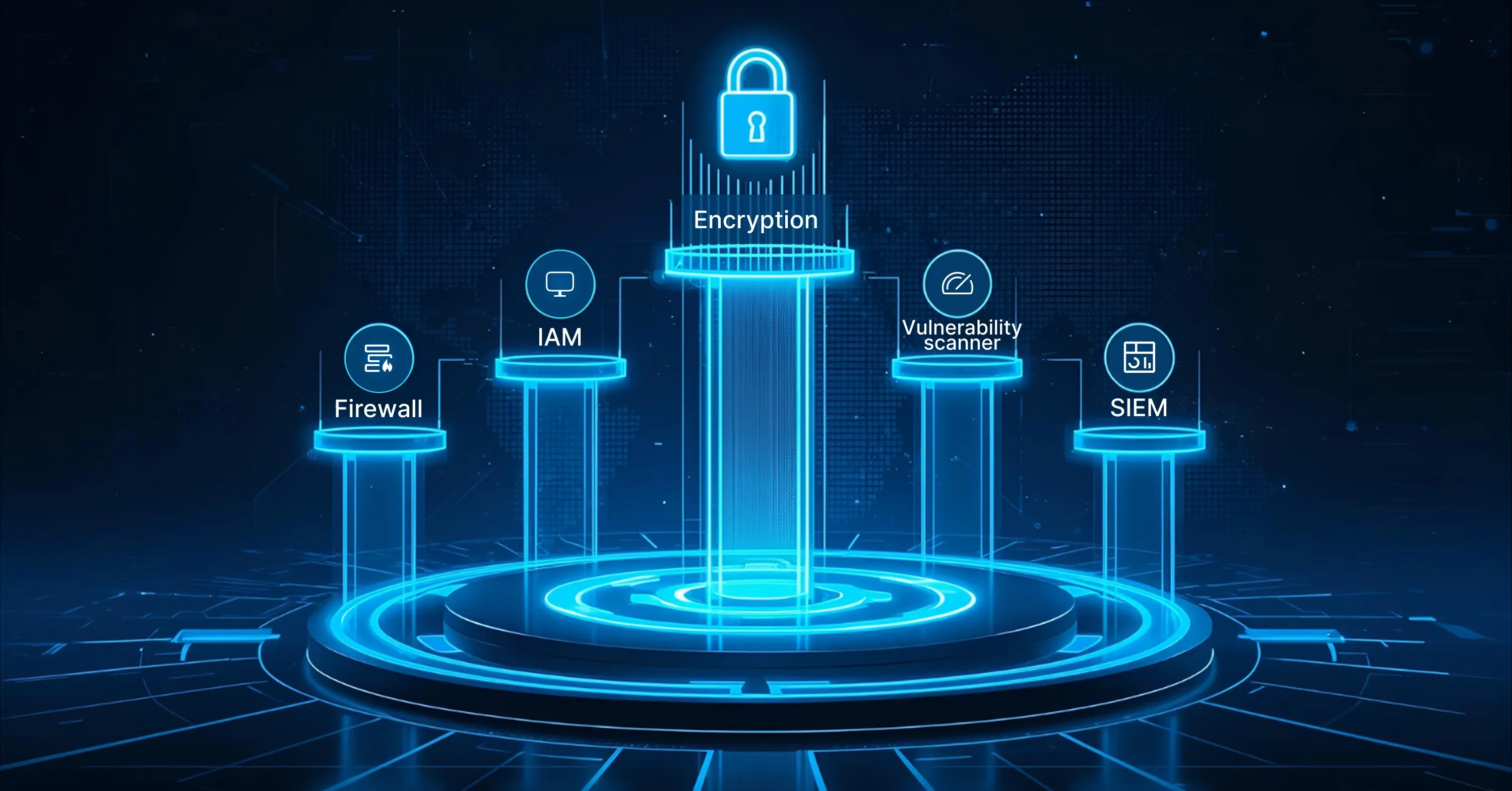

A holistic program blends technology, process, and expertise. Below are the key building blocks every cloud architect and C-level stakeholder should look for.
Managed firewalls and micro-segmentation
Even in serverless and containerized apps, network segmentation matters.
- Cloud-native firewalls centrally administered for all VPC/VNet subnets
- Layer-7 inspection to spot malicious payloads inside allowed ports
- Policy templates that match compliance frameworks out of the box
- Integration with SD-WAN to extend controls to branch offices
Keeping policies consistent prevents the classic “open port in one region, closed in another” mistake and provides a baseline for zero trust architecture.
Endpoint protection and EDR
Workstations, VMs, and Kubernetes nodes remain prime targets.
- Cloud-delivered agents offer real-time malware and ransomware defense
- Behavioral analytics detect suspicious scripts and container escapes
- Automated isolation kicks in before human analysts can react
Integrated monitoring pipelines feed endpoint telemetry into a 24×7 analysis platform for rapid triage.
Identity and access management (IAM)
Credentials drive 80% of cloud breaches. A robust IAM setup should include:
- Single sign-on (SSO) across SaaS, IaaS, and on-prem apps
- Just-in-time access with automatic revocation
- Privileged access management (PAM) vaults
- Federation with HR systems so departures instantly remove access
These steps support a zero trust mindset: never assume users or devices are safe purely because they are “inside” the network.
Data encryption and tokenization
Encrypt everything in transit and at rest, then go further.
- Customer-managed keys to satisfy sovereignty rules
- Field-level tokenization for payment or health data
- Bring your own key (BYOK) integration with major cloud KMS platforms
With consistent key management, teams avoid the trap of enabling encryption in one workload while forgetting another.
Vulnerability management and patch orchestration
Regular scanners often miss container images, serverless code, or forgotten test VMs.
- Continuous scanning across clouds, containers, and traditional servers
- Risk-based scoring so teams fix items that truly matter
- Auto-patch pipelines that tie into CI/CD for zero-touch remediation
Pairing these tools with centralized monitoring and expert review ensures critical CVEs get patched before exploitation.
SIEM, log management, and centralized monitoring
Centralized analytics are the glue that unites all pillars.
- Normalization of AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, GCP Audit Logs, and on-prem syslog into one schema
- Machine-learning detection of anomalies, insider threats, and supply-chain attacks
- 24×7 automated alerting and predefined incident workflows ensure that only verified, high-severity events reach the internal team
A leading provider of managed IT services can shoulder this workload, giving overstretched analysts room to focus on strategic initiatives. Explore more on Cloud Services and DevOps capabilities.
Backup and disaster recovery
Security is incomplete without the ability to bounce back.
- Immutable backups stored in separate cloud accounts
- Hourly snapshots for mission-critical databases
- Automated failover runbooks tested quarterly
- Ransomware-resistant storage tiers with write-once protections
This final layer ensures that, even if attackers succeed, the business survives with minimal data loss. For end-to-end guidance on backup, DR, and rapid root cause analysis, consider the recommendations laid out in our Сloud Services and DevOps.
Together, these pillars create a single security fabric that follows workloads wherever they live.
Industry-specific considerations
Regulated sectors cannot adopt a one-size-fits-all model. Below are examples of tailored needs.
Finance
- PCI DSS requires quarterly ASV scans and centralized log retention for at least one year.
- Real-time fraud analytics must ingest card telemetry without breaching customer privacy.
- Separation of duty is paramount, so IAM policies block developers from moving code to production without an approver.
Healthcare
- HIPAA and HITECH mandate encryption in transit and at rest for electronic protected health information (ePHI).
- Audit logging must track who touched every record, which drives SIEM storage costs.
- Disaster recovery objectives often cap RPO at 15 minutes for critical imaging systems.
Government
- Many agencies pursue zero trust due to the OMB M-22-09 mandate. 67% feel confident in meeting requirements, according to a Security Magazine article.
- FedRAMP authorization influences cloud provider selection and dictates regular pen-tests.
- Secure enclaves and air-gapped backups protect classified data.
Customizing controls for each vertical keeps audits smooth and reduces the chance of fines. For broader coverage of complex compliance and multi-industry support, visit Industries.
Centralized Monitoring and Incident Response
According to Gartner, worldwide spending on information security is projected to reach USD 213 billion in 2025, up from USD 193 billion in 2024. A centralized cloud-focused monitoring layer gives organizations three advantages:
- 24×7 visibility into cloud and hybrid workloads
- Faster investigation with predefined playbooks and expert responders
- Continuous tuning of detection rules as environments evolve
This model helps teams maintain strong security outcomes without the complexity of operating multiple disconnected tools.
Measuring ROI and compliance benefits
Security spending must prove value to CFOs.
- Lower breach likelihood: Consolidated controls reduce exposure surface and potential fines.
- Faster audits: Central evidence collection cuts prep time by weeks.
- Reduced staffing costs: Automated monitoring workflows and integrated patching lessen headcount needs.
- Business continuity: Immutable backups minimize revenue impact during an incident.
When presenting to executives, translate these points into hard numbers. For example, calculate the cost of one hour of downtime, then show how managed disaster recovery shrinks outage windows.
What is managed cloud security?
Managed cloud security is a subscription-based service model where a third-party provider designs, deploys, and operates unified security controls - such as firewalls, endpoint protection, IAM, zero trust policies, vulnerability scanning, SIEM, and backup - across public cloud, private cloud, and on-prem environments. The provider’s 24×7 SOC monitors events, responds to incidents, and ensures compliance, giving organizations consistent protection and visibility without the complexity of managing multiple point tools.
Conclusion
A patchwork of security tools cannot defend rapidly evolving hybrid infrastructures. By embracing a unified managed cloud security strategy - anchored by centralized monitoring, zero trust architecture, and consistent controls -enterprises gain the visibility, agility, and assurance they need to protect data and satisfy regulators.