Overview
CI/CD automation allows organizations to deliver software at speed without compromising reliability. By automating code integration, testing, and release workflows, teams reduce operational risk, improve software quality, and eliminate manual bottlenecks. The following sections break down how automated pipelines improve delivery predictability, strengthen quality controls, and reduce release risk across modern software environments.
The High Cost of Manual Delivery
The demand for rapid software updates has never been higher, forcing organizations to make difficult trade-offs. Speed often takes precedence over rigorous vetting, leading to risky deployments. In fact, research indicates that 45% of organizations now prioritize delivery speed over software quality to keep up with market demands. This rush creates a dangerous gap where stability is sacrificed for velocity.
When teams rely on manual intervention to bridge this gap, mistakes are inevitable. Human error during testing or deployment is a primary cause of downtime and defects. The data reveals a concerning trend where almost two-thirds of organizations admit to deploying code without fully testing it. Without automation to handle these repetitive checks, companies are essentially gambling with their user experience every time they release an update.
The financial consequences of these shortcuts are severe. Downtime and bugs act as a drain on revenue and resources.
To stop this cycle of risk and loss, IT leaders must move beyond manual oversight. The solution lies in building a system that enforces quality standards automatically, ensuring that speed does not come at the expense of stability.
The Cost of Shortcuts
Consider a mid-sized fintech company that relied on manual regression testing, which is the process of re-running tests to ensure new code does not break existing features. During a critical quarterly update, the team skipped several manual checks to meet a deadline. A missed bug caused transaction failures for 15% of their user base. The resulting emergency patch took three days to deploy, costing the firm significantly in customer churn and reputation damage, mirroring the statistics where financial firms face losses in the millions.
Understanding the CI/CD Engine
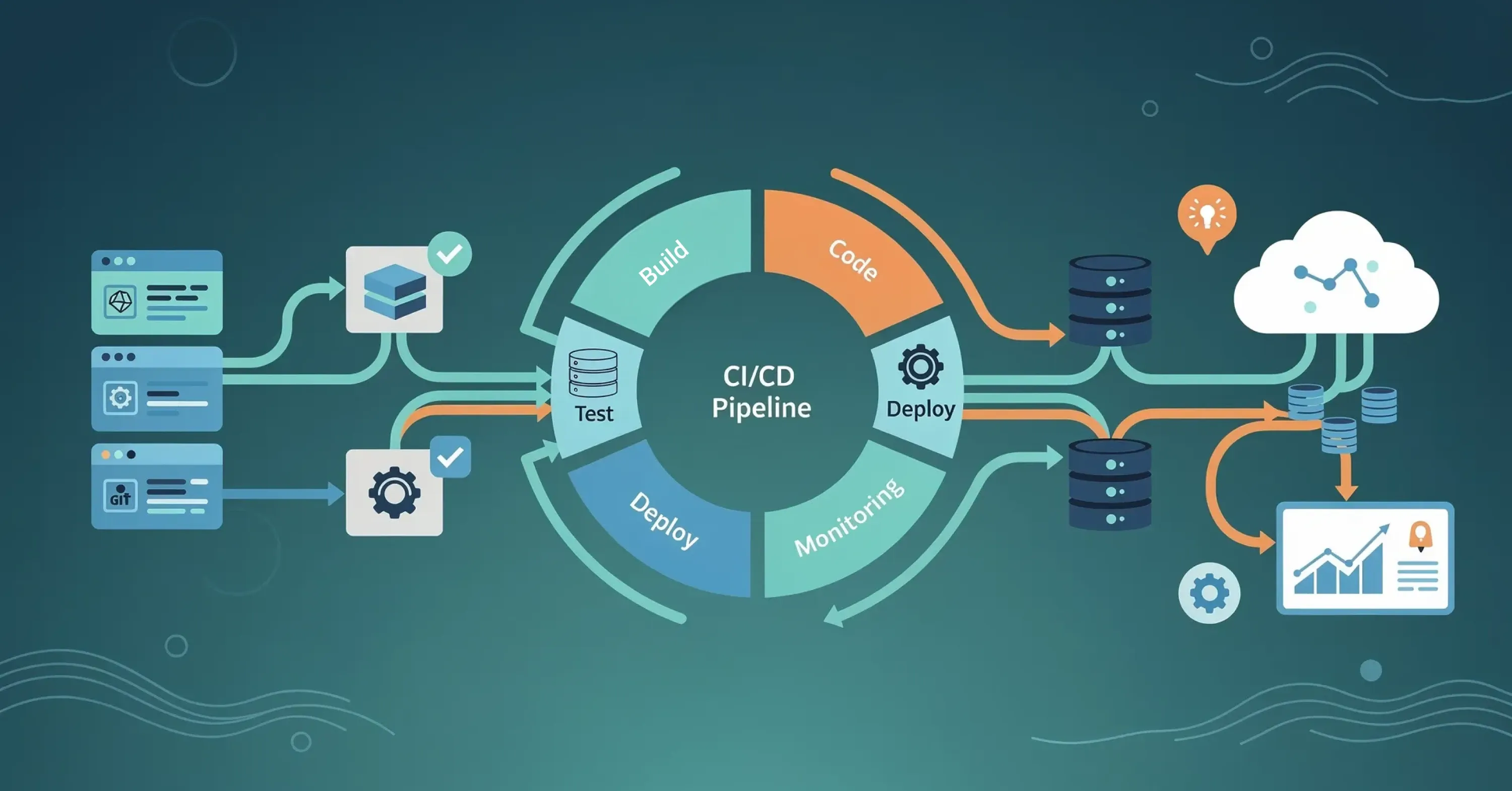
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are the twin pillars of modern DevOps. Together, they form a pipeline that automates the journey of software from a developer's laptop to a production environment. CI focuses on the frequent merging of code changes into a central repository, where automated builds and tests run immediately. This ensures that conflicts are caught early. CD extends this by automating the delivery of that code to testing and production environments.
This automation acts as a reliable engine that runs 24/7. It replaces the "heroics" of release engineers with predictable, scripted workflows.
-
Consistency: Every piece of code goes through the exact same rigorous checks.
-
Feedback: Developers receive instant alerts if their code breaks the build, allowing for immediate fixes.
-
Velocity: Teams can release updates multiple times a day rather than once a month.
By removing manual handoffs, organizations regain control over their software lifecycle. The pipeline becomes the single source of truth for the state of the application.
For a deeper perspective on moving from ad-hoc chaos to a structured DevOps model, see From Code to Customer: Accelerating Innovation with Cloud DevOps.
Supply Chain Security and SBOM
As CI/CD pipelines become the backbone of software delivery, they also play a critical role in supply chain security. Many organizations now integrate Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) generation directly into their build processes to maintain a transparent inventory of open-source and third-party components. This visibility helps teams identify vulnerable dependencies earlier, respond faster to emerging threats, and meet customer or regulatory security requirements. Embedding SBOM checks into CI workflows allows organizations to shift security left without slowing down delivery.
CI/CD Test Automation: The Quality Safety Net
The backbone of any successful pipeline is CI/CD test automation. Without automated testing, the pipeline is just a fast way to ship broken code. Automated tests act as a safety net that catches defects before they reach the customer. This is essential for reversing the trend where companies deploy untested code.
Modern testing strategies have evolved to cover complex environments. Teams are no longer testing on a single browser or device. Data shows that continuous testing teams now run automated tests on an average of 7.9 different platforms and environments. This breadth ensures that software works correctly whether a user is on a mobile phone, a tablet, or a desktop.
The efficiency of these tests determines the speed of the entire pipeline. Slow tests create bottlenecks. However, improvements in technology have drastically reduced wait times. In 2025, the average automated test execution time was 1 minute 48 seconds, representing a 41% improvement over the prior year. This speed allows developers to stay in their workflow without long interruptions.
High pass rates are another indicator of a healthy testing culture. A stable suite of tests gives stakeholders confidence in the release. Recent benchmarks show a 75% average automated test pass rate, suggesting that teams are getting better at writing reliable tests and maintaining code quality.
If you want to discover practical workflows to automate testing and delivery, check out The Managed DevOps Cheat Sheet: how to cut App Development Time and Costs by 80% about devops technology.
Solving Flaky Tests
An e-commerce platform faced issues with "flaky" tests—tests that pass or fail randomly without code changes. This unreliability caused developers to ignore test results. The team invested in stabilizing their ci cd test automation suite. They isolated the testing environments and optimized their scripts. As a result, their reliable pass rate climbed to match industry benchmarks. The engineering director could finally sign off on releases with confidence, knowing the green light from the pipeline actually meant the software was ready.
Streamlining the CI/CD Release Process
Once code passes testing, the ci cd release process takes over. This phase involves packaging the application and deploying it to servers or cloud environments. Historically, this was the most stressful part of software delivery. Ops teams would work late nights, manually copying files and restarting services, hoping nothing would crash.
Automation transforms release management into a push-button event. It allows for advanced deployment strategies that minimize risk.
-
Blue-Green Deployments: Two identical environments exist. Traffic is switched from the old version (blue) to the new version (green) instantly.
-
Canary Releases: The update is rolled out to a small percentage of users first. If no errors occur, it expands to everyone.
-
Rollbacks: If a defect is found, the system can automatically revert to the previous stable version in seconds.
These techniques decouple deployment from release. You can deploy code to production but keep it hidden behind feature flags until you are ready to "release" it to users. This granular control is vital for business continuity.
For more on release automation and deployment patterns, see Tech-Driven DevOps: How Automation is Changing Deployment.
Navigating the Toolchain and AI Adoption
The landscape of tools available for ci cd automation is vast and often fragmented. Organizations rarely rely on a single solution. Surveys indicate that 32% of organizations use two different CI/CD tools and 9% use three or more tools in their delivery processes. This complexity can be a double-edged sword, offering flexibility but increasing maintenance overhead.
Popular platforms continue to dominate specific niches. For instance, 62% of respondents use GitHub Actions for personal projects and 41% use it in their organizational CI/CD pipelines, highlighting the preference for tools that integrate closely with code repositories.
Artificial Intelligence is beginning to enter this space, primarily to help solve complex problems like debugging. Debugging failed tests is notoriously time-consuming. To address this, 70% of organizations use TestGrid’s AI-assisted failure analysis and similar tools to interpret why a test failed. However, broad adoption of AI across the entire workflow is still in its early stages. Surprisingly, 73% of respondents report not using AI in their CI/CD workflows at all, suggesting a massive opportunity for early adopters to gain a competitive edge.
To better integrate a hybrid toolchain, and manage automation at scale, see the recommendations in Cloud Services and DevOps.
Strategic Implementation for Business Growth
Implementing CI/CD automation is not just a technical upgrade; it is a strategic business initiative. It requires a cultural shift where quality, reliability, and cost awareness become shared responsibilities across engineering and operations teams. For many organizations, sustaining this level of maturity over time can be challenging due to limited internal capacity and competing priorities.
Cost-Aware Delivery and Shift-Left FinOps
As CI/CD practices mature, cost management becomes an integral part of the delivery lifecycle. A shift-left FinOps approach embeds cost visibility and financial guardrails directly into pipelines, enabling teams to identify inefficient build steps, oversized environments, or unnecessary cloud usage early in development. This helps prevent cost escalation in staging and production while keeping engineering velocity aligned with financial accountability.
At this stage, the challenge often shifts from selecting the right tools to operating and optimizing the delivery system at scale. Balancing release reliability, security controls, cost efficiency, and developer productivity requires continuous ownership and refinement.
Organizations that augment their teams with experienced delivery and operations specialists can accelerate this transition. Managed IT services provide structured support across infrastructure, cloud platforms, security, and operational optimization, helping teams maintain high-quality delivery without diverting focus from product innovation.
To explore how this model supports scalable delivery, see Managed IT Services.
Successful implementation typically starts with incremental improvements. Automating builds, introducing automated tests, and deploying to staging environments in stages allows teams to demonstrate ROI early while reducing operational risk as automation expands.
Conclusion
The path to modern software delivery is paved with automation. As we have seen, the cost of manual processes - measured in millions of dollars and lost reputation - is simply too high. By adopting ci cd automation, organizations gain the ability to balance speed with quality.
From the rigorous safety net of ci cd test automation to the efficiency of a streamlined ci cd release process, these tools empower teams to innovate without fear. To further explore how automation, cloud, and managed services work together as the new standard in digital organizations, see From Code to Customer: Accelerating Innovation with Cloud DevOps. Whether you are managing a complex financial platform or a fast-moving consumer app, the ROI of automation is clear: faster delivery, fewer outages, and a more productive engineering team. Now is the time to audit your pipelines and ensure your delivery engine is built for the future.